Type of Barcode Scanner: Which Is The Best For Your Business?
Understanding clearly type of barcode scanner will help you to choose a suitable one.
Barcode and barcode scanner are integral parts in our modern life and high-performing business.
We can see an image of a barcode reader easily from store, restaurants, libraries, supermarkets, etc.
So, how many are there barcode scanner types? How does the barcode scanner work?
Let’s dive into this article to find answers.

How many are there barcode scanner types?
What Are Barcode Scanners?
When you consider a barcode scanner, you probably see a little tool that can assist you read the lines on a label, but the mechanism is actually more complicated.
Not only capture the barcode's image, barcode scanners are designed to read barcodes, decode the data therein, and send the information to a computer.

A barcode scanner
Depending on the scanner model, this communication can be sent by connected or wireless connections.
Another way to say it is that a barcode reader inputs data significantly more quickly than a keyboard would.
The scanner easily adds data to a database or your business application rather than having to manually type the number, which is susceptible to human mistake.
How Does The Barcode Scanner Work?
How to read a barcode? Typically, a barcode scanner can scan and read barcodes with the help of a decoder and cable.
The device will read the barcode on a box or product label and then transfer the information to the decoder.
The decoder then interprets the barcode information and transmits it via cable to a connected computer system.
Some scanners are un-decoded while the decoder is built into the scanner itself.

How does the barcode scanner work?
The latter kind of kit will include a separate interface device that collects data from the scanner and feeds it into the computer.
There are two outputs available for barcode readers to connect to computers: RS232 or the keyboard wedge.
Because it lets you change data before it enters the computer system, RS232 is the more complicated of the two.
Any open serial port on a computer will allow RS232 to connect.
The keyboard wedge may connect to both a keyboard and a computer at once.
Although a keyboard wedge has an easy-to-use interface and doesn't require any software, you can't change the barcode data before it is input into the device.
Types of Barcode Scanners
There are many different type of scanners available today, both stationary and portable.
To decide which type and format would make the ideal barcode scanner for your retail business or company, read the following barcode scanner buying guide:
-
Laser scanners
-
Image scanners
-
2D area imagers
-
CCD barcode scanners
-
Pen Readers and Barcode Wands
Laser scanners
One of the more sophisticated technologies for reading barcodes is the laser scanner.
This kind of scanner uses a laser to read barcodes by using a series of mirrors or prisms to reflect light.
Laser scanners can read linear 1D barcodes from a distance of up to two feet and are made specifically for this purpose.

Laser scanners
As a result, laser scanners have more internal moving glass or plastic components than image scanners, which makes them more prone to breakage.
These barcode scanners work similarly to pen readers, with the exception of the laser.
Image scanners
A small digital camera is used by an image-based barcode scanner to take a picture of the barcode.
An associated computer system scans and reads the collected image for inventory reasons.
A normal image scanner can only read barcodes from a few inches away, while more recent devices like the Honeywell 1300g are now more competitive with the average laser scanner in terms of reading distance.

Digital scanner
The top barcode scanners for small businesses as well as larger companies in the field service, warehouse, and logistics sectors include Honeywell models.
Image scanners are less susceptible to impact damage than laser scanners because of the simple internal camera mechanics.
Image scanners, like laser scanners, are designed only to read 1D barcodes.
2D area imagers
A 2D image scanner is quite similar to a standard image scanner, with the exception that it can scan all sorts of barcodes, including 1D, 2D, and stacked barcodes.
A 2D imager makes it easier to read barcodes because the code can pass through the scanner horizontally, vertically, upside-down, or right-side-up.
A barcode can only be read by laser and traditional image scanners when it is held horizontally across the capturing eyes.

2D area imager
As a result, scanning objects can be done much more quickly and easily than with a 2D imager.
A barcode can also be read off non-label surfaces, such as smartphones and computer screens, using some 2D imagers, like the Honeywell 1900.
CCD barcode scanners
A row of tiny sensors are installed in the front of Charge Coupled Devices (CCD) barcode scanners.
Waveforms generated by the CCD scanner correspond to specific bars and spaces, and this data is decoded within the scanner before being transmitted to the computer system.
A CCD scanner measures ambient light that is emitted from the barcode, as opposed to laser and pen scanners that measure frequencies of reflected light inside the scanner.

CCD barcode scanner
Pen Readers and Barcode Wands
The tip of a pen or wand barcode reader has a light source and a photodiode.
A waveform that corresponds to the width of specific gaps and bars is formed when a barcode is dragged over it.
This information is then decoded and fed into the computer system.

Pen Reader and Barcode Wand
Different Barcode Scanners Format
The following step is to select the most appropriate form of the scanner you've chosen, having first decided which type best suits your company's requirements.
You will probably prefer a set of stationary, plug-in scanning equipment if you operate a conventionally laid up storefront with checkout terminals.
In contrast, a large floor with a lot of heavy items may call for cordless scanners.
Thankfully, the 5 types of scanners available today may satisfy a variety of needs:
-
Handheld
-
Presentation
-
Mobile units
-
In-Counter Scanners
-
Fixed Mount
Handheld
The most popular type of scanners are handhelds, which are available in both corded and cordless versions.
Handheld scanners are simple to use; all you need to do is hold the scanner around your hand, point it at a barcode, and push a button.

Handheld
Some handheld variants have stands, allowing for hands-free operation.
All fields where barcodes are used, such as grocery stores, warehouses, field services, and healthcare institutions, can benefit from using handheld scanners.
Presentation
Wide-area reading at a fixed location is the purpose of presentation scanners.
Designed to be set up on a countertop, a presentation scanner can be used to scan the barcodes on any items you pass by.
There's no need for pointing, unlike with handheld scanners.
Simply place the barcode on each item in front of the presentation reader, which will swiftly and effortlessly scan the code.
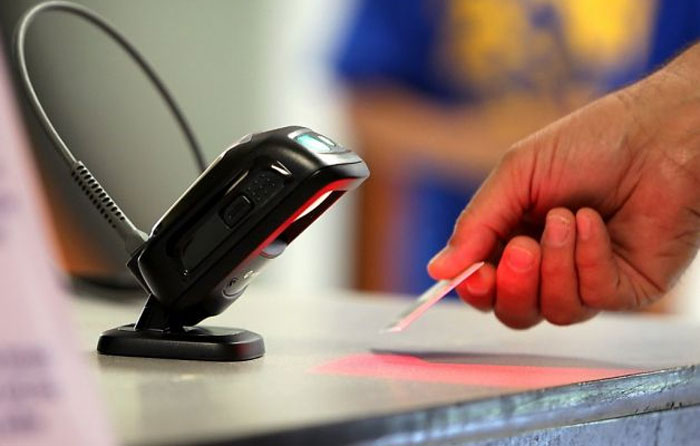

Presentation
Retail store checkout counters frequently have presentation scanners there.
Presentation scanners like the Metrologic MS7580 can read a variety of barcodes simultaneously because of their extensive scanning capabilities.
Metrologic provides some of the top barcode scanners for field service, medical records, and retail establishments, with a variety of models to select from.
Mobile units
Business people can scan barcodes using handheld computers, even though they are intended for much more than just that.
Anywhere there is Wi-Fi or cellular (WAN) coverage, they are unrestricted by cords or large fixed devices.
Inventory staff working on the floors of huge department warehouses with long rows of heavy things may find this to be of particular help.
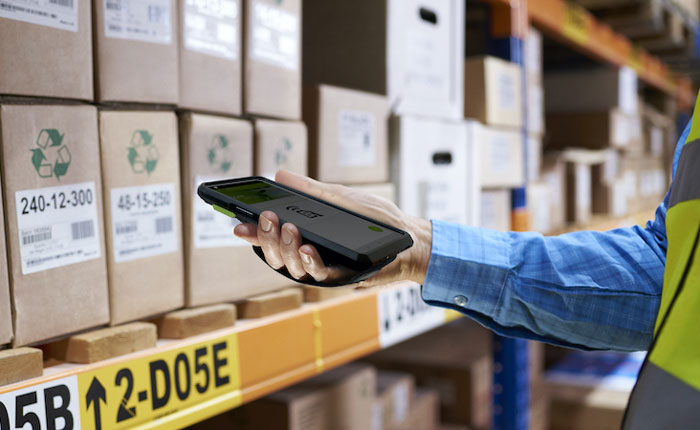

Mobile units
Barcodes may be read by a handheld app from any point on a warehouse floor and remotely recorded into a business's computer system, eliminating the need to move everything through the same check-in and checkout terminals.
Additionally, mobile devices enable barcode reading in outlying areas where larger, plug-in variety scanning systems would be impracticable.
A mobile device can save the information from each barcode scan even in places outside of Wi-Fi range for later inclusion into a business's inventory data system.
In-Counter Scanners
An in-counter scanner is a stationary device, similar to the presentation scanner, that enables salespeople and consumers to quickly and easily scan barcodes. The distinction is that an in-counter scanner in this instance is made to be included into the top of a checkout counter.
As a result, grocery store checkout and self-service lanes frequently have in-counter scanners.
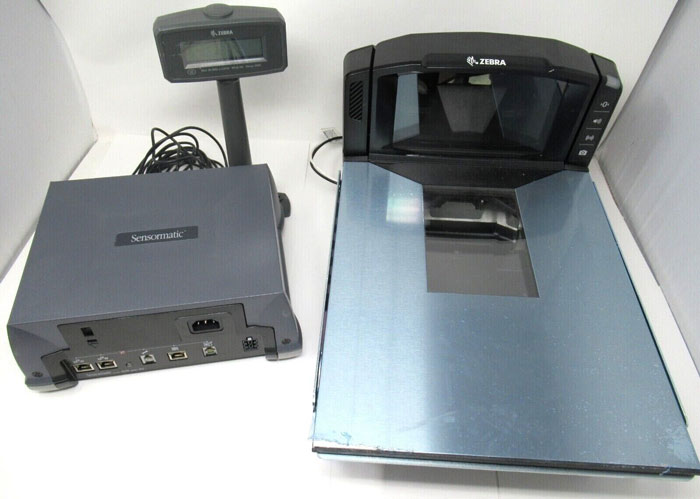

In-Counter scanner
The Datalogic Magellan 8300, one of the more well-liked in-counter scanners, enables simple integration and operation in any indoor situation.
Datalogic has some of the best barcode scanners for logistics in every type of organization, whether you need one for a small retail operation or a larger one.
Fixed Mount
Fixed-mount scanners are created for integration into substantial automation systems and are intended for more specialized applications including warehousing, manufacturing, and logistics.
This kind of scanner is typically built within a kiosk or perched over a conveyor belt.

Fixed mount
A fixed-mount scanner can read codes automatically without the need for manual triggers or button presses and is available in a variety of speeds.
Therefore, the fixed scanner makes it easy to enter data for big backroom inventory, which may be done along conveyor belts without the need for a human.
Where Are Barcode Scanners Used?
Almost every imaginable sector and application uses barcode scanners nowadays.
These gadgets, for instance, are employed in:
-
Retail for transportation, customer loyalty programs, inventory, warehouse operations, point-of-sale transactions, and more.
-
Patient admissions, bedside medication verification, lab specimen track and trace, shipping and receiving, document and record tracking, and staff communication all fall under the category of healthcare.
-
Production for work-in-progress tracking, shipping and receiving, compliance labeling, and asset management.
-
Using warehouse distribution, workflow processes including picking, putting away, stock replenishment, shipping, and receiving may be automated and optimized.
-
Cross-docking, fleet management, and pick-up and delivery services are just a few of the transportation and logistics techniques used to trace every item across the supply chain.
-
Groceries for point-of-sale transactions, stock for warehousing operations, and supplies for delivery.
-
The distribution and packaging of food once it leaves the production line. Track-and-trace regulations for food safety in the sector are constantly expanding. Companies in the food industry are required to be able to specify the times, locations, and people who handled, stored, transported, consumed, and disposed of produce and to be able to show written documentation to support their claims.
-
Applications for the field to barcoding system for small business, conduct building, machinery, and vending machine inspections, collect readings for utility companies, and more.
-
Education for staff communication, asset monitoring, attendance, registration, and document and record tracking.
-
All flats, letters, and packages with barcodes are scanned by postal and package delivery services as they enter the mail stream, and those goods are then tracked by additional scans all the way to the delivery location. The success of real-time visibility depends heavily on scanning precision.
-
E-commerce is used for many different things, including order fulfillment, marketing, shipping, inventory management, and warehouse operations.
-
Military for tracking supplies and equipment, managing IDs, managing the supply chain and logistics, managing commissaries, maintenance and repair, and other purposes.
Where are barcode scanners used?

One-dimensional (1D) barcodes, which are frequently found on consumer goods, are horizontal linear codes with variable-width lines and gaps distributed from left to right.
The 2D (two-dimensional) barcode, which resembles a square or rectangle and is read in two dimensions as opposed to the 1D barcode, which is read horizontally, stores data both horizontally and vertically (INSERT IMAGE).
An item's "license plate" is essentially translated from a 1D barcode into alphanumeric digits (i.e., numbers and letters) when it is decoded.
This information can then be linked to item-specific data, like the price, the number of goods in stock, the item description, and the item image, once it is delivered to the computer database.
A 2D barcode can encode binary data such as images, prices, website addresses, audio, and other sorts of data in addition to alphanumeric data.
The early 1D barcode scanners were laser models.
The width and arrangement of the black and white stripes are detected by the scanner, which translates them into decimal values.
A digital camera-like feature is present in the 2D imager barcode scanner.
The imager barcode scanner captures a picture instead of utilizing a laser, and then utilizes a decoding algorithm to find the barcode inside the image and then decode the data from that barcode within the image.
It is difficult to determine which type scanner is best. But the most popular one is handheld. Handheld barcode scanners can be tethered or cordless (wireless) and have a number of uses.
Five Pointers for Choosing the Best Barcode Scanner
Think about your flooring.
Consider air quality.
What is the Lighting Situation?
What Keyboard Should You Use
Which Kind of Barcodes Will You Scan
The Bottom Line
You now know everything there is to know about barcode scanners, type of barcode scanner and format. Hope you learn enough about yourself to make a good decision.
![Scan Clothing Barcode: Get Best Code for Your Item [with Benefits]](https://barcodelive.org/filemanager/data-images/imgs/20221125/Scan-Clothing-Barcode.jpg)
![Drivers License Barcode to Avoid Identity Theft [DISCLOSED]](https://barcodelive.org/filemanager/data-images/imgs/20221116/Drivers-License-Barcode.jpg)

17 Comments
Ellis Hudson
Bluetooth Wireless Barcode is the ideal barcode solution for any business due to its versatility, seamless connectivity, and efficient data transfer capabilities, making inventory management and data collection more convenient and streamlined.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Thank you
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Cooper Collins
Can handheld laser barcode scanners damage your eyes due to reflectance off the item being scanned?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Technically, it could happen if you tried to scan a concave telescope mirror at exactly the right spot to image the holographic optical element on your retina. And you held it in that spot for a whole second without blinking
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Nico Hale
Can a non-laser barcode scanner (used in McDonald’s) emit dangerous invisible radiation which causes cancer?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
No, but be careful if you are wearing stripes, you may be scanned and charged
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Cristian Cook
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using laser barcode scanners as opposed to other types (e.g., CCD)?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
The laser ones tend to be picky. If the barcode is a little too small or there’s any flaw it won’t read them
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Solomon Campbell
Good content but I will give it a 10 if you tell me how to choose the best scanner
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Hi, the answer is that is that it depends on your needs and what you use it for
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Christian Mitchell
Why do barcode scanners use red light?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
In principle one could use infrared lasers - but it would make eye situation more worrying since you cannot see it. Green, blue, UV laser that appear recently in principle can be used but would be much worse regarding cost, eye safety.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Christian Mitchell
Thanks for your reply. I've learned something new :D
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Kiara Morales
Excellent article
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Thanks
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Mila Fleming
Can the 1-Dimensional barcode readers read any type of 1D barcode? For example, can the barcode reader at the Point Of Sale read barcodes of type code 39?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Most barcode scanners are programmable with the ability to enable or disable different barcode formats
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *