Barcode Identifiers: What Are They & How to Use Them Properly
This post will discuss everything about barcode identifiers, from their definition to their uses in GS1 barcodes.
Let’s dive in!

What is a barcode format identifier?
What Are GS1 Application Barcode Identifiers?
GS1 Application Identifiers (AIs) are numerical prefixes that specify the meaning, format, and length of encoded data items.
They are used to decipher the information encoded in a barcode.
All GS1 Application Identifiers are cataloged in the GS1 General Specifications.
If the batch number is 10, for instance, the AI will be 10, and the batch code will be an alphanumeric string no longer than 20 characters long.
Several facts about GS1:
-
Multiple pieces of information can be stored in certain types of GS1 codes. AIs are required in these type of barcodes in order to qualify the meaning of each data element.
-
Data items in the user's memory bank can be encoded using GS1 Application Identifiers, which are also utilized in EPC/RFID tags.
-
There are over a hundred different GS1 Application Identifiers (AIs). A typical Application Identifier has between two and four numbers.

Everything about GS1 Application Barcode Identifiers
What Are The Uses Of Application Identifiers In GS1 Barcodes?
Below are some practices of GS1 Application Identifiers, let’s see what they are!
-
Application identifiers are used to display the meaning of a barcode.
-
They are required in the GS1 barcode standards, including: GS1-128, GS1 DataBar, GS1 DataMatrix and GS1 QR Code.
-
To promote human readable interpretation, the GS1 standard requires barcodes to have a textual representation. The AI codes must be placed in parenthesis in this text.
Keep in mind that the AIs are encoded without parentheses in the barcode.
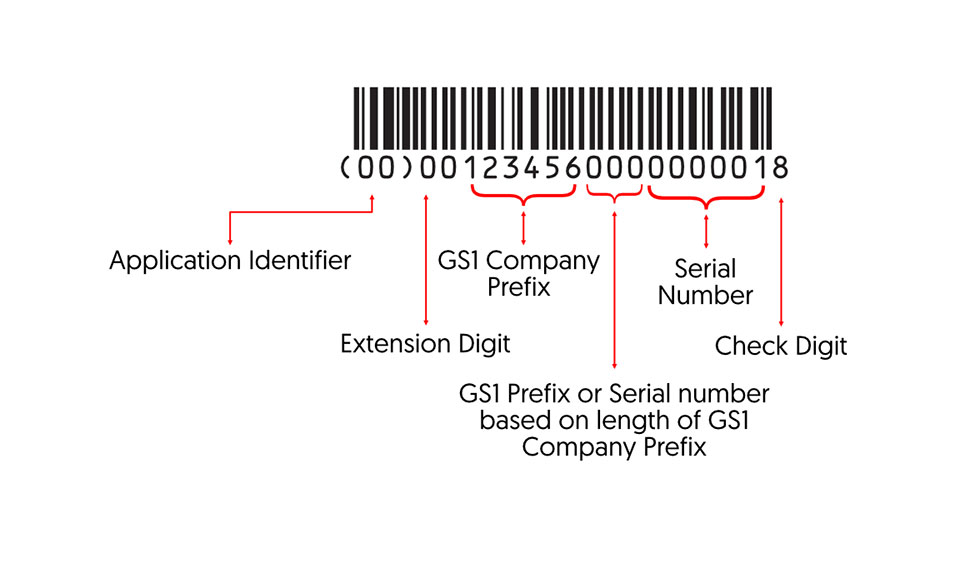
Uses of GS1 AI
How To Use GS1 Application Barcode Identifiers?
A GS1 Application Identifier and a GS1 AI data field are combined to form an element string.
Following an AI, data can be alphabetic or numeric, with fixed or variable lengths. As a field separator, the symbology character FNC1 is utilized.
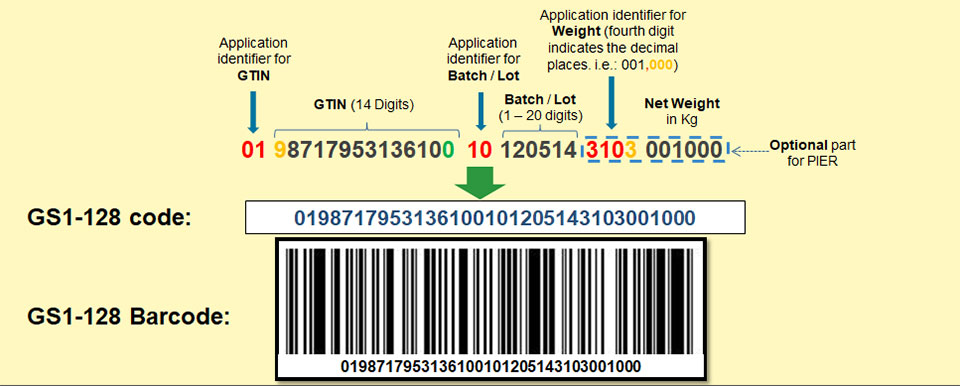
A guide to using GS1 application barcode type identifiers
-
If an AI has a length type that varies, the field must be terminated with FNC1.
-
The escape sequence "F" is used in the barcode data to specify FNC1. To encode the FNC1, turn on Translate Escape Sequences in the bar code generator.
-
There are AIs with extra grammar constraints, such as numerical exclusively
-
Only use FNC1 with variable length data fields, and leave it out after the last data field.
-
It should be noted that some applications that use GS1 DataMatrix require an ASCII Code 1DHex instead of FNC1.
*Note: Avoid encoding the brackets that are commonly used to represent an Application Identifier. The brackets for the human-readable text are generated automatically by the TEC-IT program. The brackets are not encoded within the barcode!
See also: A Full Guide On Barcode Symbologies No One Would Tell You
Examples Of GS1 Application Barcode Identifiers
Here is a GS1 AI list:
| AI | Name | Format | Date Title |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AI 00 |
SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code) |
n2+n18 |
SSCC |
|
AI 01 |
Global Trade Item Number |
n2+n14 |
GTIN |
|
AI 02 |
GTIN of Trade Items Contained in a logistic unit |
n2+n14 |
CONTENT |
|
AI 10 |
Batch or lot number |
n2+an..20 |
BATCH/LOT |
|
AI 11 |
Production date (YYMMDD) |
n2+n6 |
PROD DATE |
|
AI 12 |
Due date (YYMMDD) |
n2+n6 |
DUE DATE |
|
AI 13 |
Packaging date (YYMMDD) |
n2+n6 |
PACK DATE |
|
AI 15 |
Best before date (YYMMDD) |
n2+n6 |
BEST BEFORE or SELL BY |
|
AI 17 |
Expiration date (YYMMDD) |
n2+n6 |
USE BY OR EXPIRY |
|
AI 20 |
Product variant |
n2+n2 |
VARIANT |
|
AI 30 |
Variable count |
n2+n..8 |
VAR. COUNT |
|
AI 37 |
Count of trade items contained in a logistic unit |
n2+n..8 |
COUNT |
GS1 is a non-profit global organization with 100 member countries worldwide.
It maintains barcodes standards, RFID tags, and supply chain messaging such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
GS1 is in charge of the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) system, which is used to identify firms and their products and services in UPC, EAN, other barcodes and electronic product codes
GS1 is a global standards body that manages UPC (GTIN barcodes) identification criteria and licenses brand-specific UPC Company Prefixes or single-issue GTINs (s).
Whereas, UPC stands for Universal Product Code, a widely used barcode in the world, appearing on nearly every product in both physical and online businesses.
Customers may request that you include a U.P.C. barcode on your items or packages.
An application Identifier is a numerical prefix to a data string that specifies how that string is to be interpreted.
The data size is also revealed. Numerous Application Identifiers, like serial number and best-before date, are defined by the GS1 standards.
Data fields specified by some Application Identifiers have a predetermined length, while those specified by others have a more flexible length.
How to find my GS1 barcode?
To identify the type of barcodes (barcode symbologies), you simply need to scan the barcode using the Barcode Decoder Verification App, which recognizes common type of barcodes and recommends goods that create that type.
Examining the start and stop characters in 1D symbols (marked in red) at the beginning and finish of the following barcode instances is also a manual method.
The unique patterns of 2D symbols can be used to identify them.
Conclusion
The GS1 Application Identifiers give an open standard that may be used and understood by any organizations in the trading chain, regardless of who issued the codes initially. Hopefully, with this knowledge on barcode identifiers, you can better use them for the right purposes.
Sources:
https://www.gs1us.org/content/dam/gs1us/documents/industries-insights/standards/GS1-Application-Identifiers.pdf
https://www.barcodefaq.com/barcode-properties/definitions/gs1-application-identifiers/
https://www.barcodefaq.com/barcode-match/
![Barcode Sizes Explained & FAQs: An Ultimate Guide [The Latest]](https://barcodelive.org/filemanager/data-images/imgs/20221031/Barcode-Sizes-Tutorial_1.jpg)

9 Comments
Aubree Ward
What do GS1 barcodes contain?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
They are used to encode information such as key identifiers (product, shipment, location, etc.) and key attributes (serial numbers, batch/lot numbers, dates, etc.)
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Malcolm Newman
Great content, congrats!! Love your work! It's hard to find information about barcode identifiers on the Internet until I read your post
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Agree! I spent days writing this post although it turned out shorter than I expected
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Malcolm Newman
But still full of content!
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Daxton Castillo
Are GS1 barcodes universal?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
Yes, your barcodes and unique numbers will be accepted by major retailers and distributors all over the world
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Evelyn Walker
What are the three GS1 EDI standards?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Barcodelive
GS1 has currently three sets of EDI standards which include: GS1 EANCOM® GS1 XML. GS1 UN/CEFACT XML
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *